Cantonese temple at Sims Drive and pre-war bungalows at Adam Park identified for conservation

SINGAPORE: One of the oldest Chinese temples in Singapore may be considered for protection, along with 19 pre-war houses at Adam Park.  ,
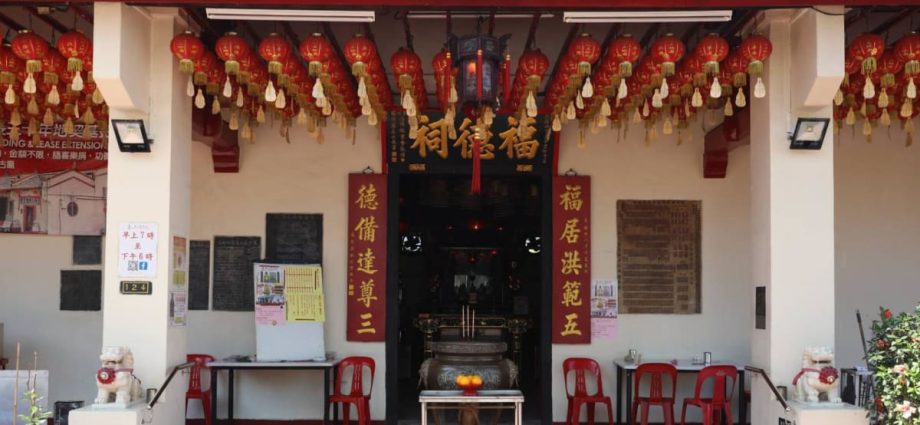
In the 1860s, migrant populations with primarily Chinese nature founded the Mun San San Fook Tuck Chee church at Sims Drive. When its directors purchased the land in 1902 to build the sanctuary along the banks of the Kallang River, it relocated to where it is now.  ,
The pre-war bungalows at Adam Park, meanwhile, were built in 1929 by the Singapore Improvement Trust ( SIT ) as housing for , families of officers from the Municipal Council and SIT.
According to the Urban Redevelopment Authority ( URA ), they have largely been preserved since World War II.
National Development Minister Desmond Lee announced the URA’s plan to preserve the two sites on Friday ( Nov 8 ), stating that Singapore must strive to include significant heritage in its development plans even as it plans for its future.  ,
At the URA Architectural Heritage Awards, he stated that “preserving buildings and structures of the highest value is an important way to do but” to provide a natural and physical connection to our history.
By conserving these structures and houses, we hope to preserve natural representations of the shared history and memories of our country, populations, and people.
This strengthens our shared nationwide personality and creates a deeper relationship among Singapore.
Conserved properties are subject to particular URA rules. Before all changes functions and new uses of the place you start, permission is required.