Donald Trump, the candidate for president of the United States, stepped up his America First campaign earlier this month by promising to impose 100 % tariffs on goods from any country that deviates from the dollar.  ,
Trump did not explain to his supporters that the dollar-protection measure did cause American households to suffer as some consumer goods are likely to cost more than double. Around 70 % of products sold at Walmart and Target are sourced from China, the country at the forefront of de-dollarization.
Trump made his announcement on the day of the very anticipated monthly BRICS conference, scheduled for October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia. The appointment may make an announcement regarding a strategy for the creation of a viable alternative to the current dollar-centric global financial system.
Although more information are still being provided, some observers anticipate that the conference will make an announcement regarding a multicurrency payment system. Some BRICS watchers even anticipate the release of a blueprint for a trading currency with gold backing.
Bretton Woods
For a number of reasons, the development of an alternative to the current money method would be traditional. It may mark the initial legitimate attempt to depart from the Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944, which established the post global financial system.

The money was subject to the predetermined price of gold under Bretton Woods, while all other currencies were fixed at the money. At the so-called golden windows, countries with dollar-denominated trade deficits could exchange their money for gold with the US central banks.
Financial security was achieved by the money system, but almost all of it was controlled by the US. US businesses evolved into the hubs of international commerce. A Chinese company that purchased products from India had to purchase dollars to spend its Indian dealer. The US was able to impose any man, business, or nation on the global financial system thanks to the unified system.
When US President Richard Nixon decoupled the dollar from silver in 1971, Bretton Woods began to unravel. The US chose to close the silver screen rather than compromise its business, efficiently defaulting on its Bretton Woods responsibility, as the country faced rising trade deficits.
The choice had big implications. The US government lost its fiscal discipline after being freed from the restrictions imposed by the gold standard and embarked on a decades-long spending binge. From 1971 to 2024, the US national debt grew from$ 400 billion to$ 35 trillion.
A growing number of prominent economists and business officials have sounded the alarm because servicing the national debt has grown to be the most important line item on the US federal budget, even more so than yearly defence spending. Tesla CEO Elon Musk just warned:” At current levels of government saving, America is in the fast lane to bankruptcy”.
More precisely, the US may immediately work out of lenders willing to buy its debts. In recent years, China has sold US Treasuries worth hundreds of billions, and foreign investors have recently become online retailers of US loan. ( The commonly used term “printing money” actually means issuing debt. )
BRICS versus G7
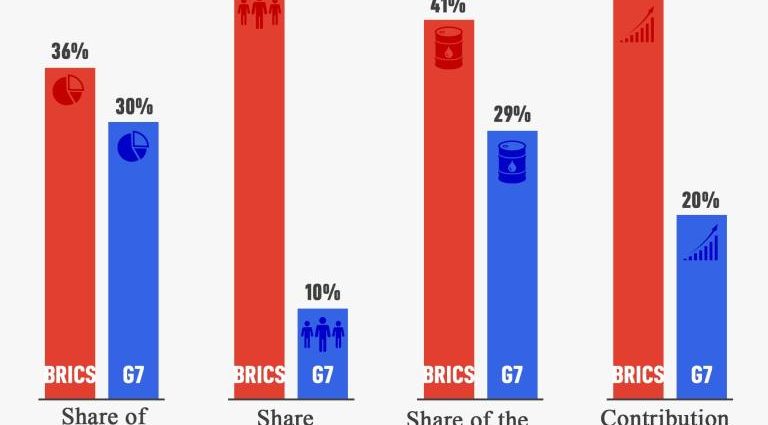
Even without the US incurring its huge debt, continuous de-dollarization is obvious. The National share of the world economy is rapidly declining.
In 2016, BRICS states overtook the G7 in combined GDP. The group now accounts for 35 % of the world’s output, compared to the G7’s 30 %. China contributes almost twice as much to the world’s industrial output as China alone, nearly twice the US.

There are many different themes, but it’s challenging to design a financial or monetary structures for nations as varied as the BRICS members. Sergei Ryabkov, the deputy foreign secretary of the Russian Federation, just demanded a financial unit akin to the Western Currency Unit (ECU), the euro’s precursor.
The ECU was conceived in 1979 in response to Nixon’s decision to close the silver screen. The German dollar started to shift wildly as it was no more pegged to gold. Therefore, the ECU established a common unit of account that stabilized forex markets.
The “bancor,” a dollar system that economist John Maynard Keynes suggested during the Bretton Woods Conference, is another example of how things are being used.
The bancor was conceived by Keynes as a global unit of account tied to a pantheon of essential goods like oil and grains. This would guarantee that the bancor’s value was determined by real financial resources more than fluctuating national economies.
In an effort to promote healthy global trade, Keynes even suggested sanctions for nations with prolonged trade surpluses or deficits. The US criticized the bancor as troublesome and preventing free business. But today’s severe imbalances—particularly the US’s huge trade deficit with China—validate Keynes’s vision.
An mBridge not too far
China is working with a number of other nations on mBridge, a blockchain-based platform that supports fiscal transactions in several currencies, despite the possibility of a BRICS frequent money in the near future.
Simultaneously developed by the central bankers of China, Thailand, the UAE and Hong Kong, mBridge helps fast, peer-to-peer deals without third-party presence. According to reports, the platform supports Central Bank Digital Currencies ( CBDC ) and uses blockchain technology that is similar to Ethereum.

Cross-border business finance is made more cost-effective and affordable by the mBridge. A Thai firm may exchange rice for a businessman in Singapore in Thai ringgit or any other agreed-upon money. Transactions are quick and do n’t involve third parties. In mBridge, institutions of participating nations are the nodes in the network.
BRICS now comprises nine countries, the initial five members of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa plus Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran and the UAE. Some have speculated that the gathering might eventually expand to include more than 100 nations, while over 40 extra nations have expressed interest in joining.
However, the BRICS surprised the world last month by announcing that it would quit accepting new people for a short time. No justification was given, but the ice might be related to the difficulty and awareness of developing a new financial infrastructure and its possible worldwide influence.
BRICS has plenty of reasons to tread carefully. Global financial markets could become unstable if only a new monetary system’s future roadmap was announced. Obviously, the group will want to avoid accusations of triggering a financial crisis.
The direction BRICS will take from here will depend on several factors. How aggressively will the US defend the dollar? How will the US address the country’s growing trade and debt problems? What will the country’s increasingly dysfunctional political system do next?
While Trump’s pledge to sanction de-dollarizing nations could be campaign rhetoric, an escalation of America’s sanctions war could trigger a financial reset in response.
BRICS might decide to establish a currency unit that is partially supported by gold and other natural resources, including oil, minerals, and metals. Given that it controls a sizable portion of the world’s natural resources and is able to influence global prices, the group has considerable leverage.
One way to tell BRICS is gearing up for a similar financial reset is its unheard of hoard of gold. BRICS members have purchased gold at record prices in the past two years. Following a financial or monetary crisis, the monetary metal has historically been used to rebalance currencies.
To be sure, a transformation of the now 80-year-old global financial system is inevitable. In a neo-colonial transformation of the British Empire, Bretton Woods modernized the banking system and moved London to New York as the seat of power.
On the other hand, the BRICS will likely work from the ground up to create a new financial system that is based on the demographic and economic realities of the 21st century, rather than the 20th.