Central bank digital currencies( CBDCs ) are being internationalized by central banks and financial institutions all over the world. Cross-border payments will be able to be processed in real time by the global community. The” parallelization” of all marketable goods, from stocks and real estate to gold, could be the next step.
Electronic currencies that are kept on a record kept by central banks will take the place of money in the upcoming years as CBDCs. Users can download a modern finances to their mobile device to access their salaries and make purchases of goods and services. Users would be able to quickly transfer money to another digital wallets anywhere in the world thanks to a worldwide CBDC network.
China is at the forefront of CBDC implementation. Currently, the e-yuan is accessible in 26 locations and 17 Chinese regions. The People’s Bank of China ( PBOC ) digital wallet has been downloaded by more than 250 million people. To promote the use of CBDCs, regional institutions and state-owned businesses are paying pay in digital yuan.
Testing for internationalizing CBDCs are currently being conducted. The International Monetary Fund ( IMF ), the Bank for International Settlements, the PBOC, and other monetary authorities are constructing the” rails” that will enable the interoperation of CBDC platforms. Cross-border payments may be made possible by a worldwide system of CBDC planforms in real time and at no cost to the consumer.
To validate transactions of crypto coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum, CBDCs use a modified version of blockchain, the distributed( non-centralized ) ledger technology. Contrary to bitcoin, central banks’ CBDC programs are centralized. Platforms for CBDC are governed by the federal institutions.

After European nations barred Russia from SWIFT, the Belgium-based world messaging service for business banks, developing an international CBDC network became more urgent last year. SWIFT effectively has a stranglehold on cross-border pay deals worldwide.
Concerns about the rest of the world, particularly in the Global South, were raised by Russia’s rejection from SWIFT. Any nation that violates European policies could be the next to have its payment system banned if a major global power like Russia were to do so.

The militarization of SWIFT and the seizure of US$ 300 billion in Russian money deposits even gave BRICS, the loosely connected association of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, fresh momentum.
BRICS hardly ever garnered media attention before late. However, more than 50 nations in the Global South applied for account following the economic war on Russia.
The financial system’s weaponization has resulted in a rise in the number of” equal – to peer” cross-border pay agreements. Countries are avoiding SWIFT and the world dollars system by trading in their own currencies more frequently. Cross-border bills from peer to peer are immune to American sanctions.
The debt levels of the developed markets are another issue facing BRICS and the Global South. The Group of Seven nations are submerged in a sea of debts. Over$ 32 trillion, or 120 % of GDP, is owed by the US alone. The largest object in the US budget will soon be curiosity payment on the national debt.
There are indications of a decline in confidence in the money everyday. Record amounts of US debt( treasuries ) are being sold by China, Japan, and Saudi Arabia. The money is being reinvested by China in Middle Eastern oil fields. Central banks all over the world are purchasing metal in record sums at the same time.
In the past, gold has served as a safeguard against currency depreciation( feasional inflation ). However, in the event that currencies fail, it can also be used to update and recalibrate the financial system.

Key bankers, who have a more in-depth understanding of the financial system than most, have made significant gold purchases, indicating that they believe financial resets are actually possible. Supply assets typically have a lifespan of approximately 100 years, according to record. In addition to & nbsp,
The Modern Monetary Theory( MMT ), which was developed 40 years ago and is predicated on the idea that governments issuing their own currency can never go bankrupt, would also suffer from a new gold standard. Governments can usually print more money, according to MMT. However, that presupposes the business is a closed, self-contained system. & nbsp,
The US is perpetually in the trade shortage and owes trillions of dollars in foreign debts, or roughly 60 % of its GDP. It has already been established that its international creditors have a finite compassion for printing endless amounts of money. History demonstrates that the fate of a reserve currency is frequently accompanied by the currency’s depreciation.
Since the late US president Richard Nixon removed it from the gold standard in 1971, the dollar has lost more than 90 % of its price when compared to gold. The US government is free to print as much money as it wants, but a gold-based currency restore may make it clear that it cannot write gold, rare earths, or oil.
Tokenization
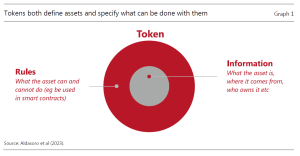
CBDCs are” tokens” of money, just like coins. A linear wire( a block of data ) that is specific to that particular currency system serves as their representation. The central bank’s register contains the block of data.
Another tradable assets may be tokenized if currencies is. Equities, insurance policies, house titles, and anything else with pecuniary value are all being considered for tokenization by central banks. All of the necessary information for that property is contained in the coin.
A tokenized insurance policy, for example, includes information about the coverage( terms and conditions, validity date, etc. ) and who is permitted to socialize with the item. To help registration payments, the block may have access to the policyholder’s bank account.

By connecting CBDC wallets to insurance policies, tax returns, credit histories, and other assets and transactions, a so-called unified ledger — a single register of all the owner’s assets or transactions— is produced. & nbsp,
Additionally, a tokenized CBDC program you support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Stable Coin. While some central banks may forbid cryptocurrency trading and the transformation of CBDC assets, others may permit it. Like that of various resources, the fluctuating price of cryptocurrencies can remain updated in real time.
Integrated accounting records
A Blueprint for the Future Monetary System was the title of a talk given by Hyun Song Shin, head of research at the Bank for International Settlements, this season. The report’s essential points were listed in the section on tokenization:
- A consolidated record, a new kind of financial market infrastructure, had combine tokenized assets, tokenised deposits, and money from central banks to fully benefit from tokenization.
- Many ledgers, each with a particular use case, may co-exist, connected by application programming interfaces to ensure connectivity and encourage financial inclusion and an equal playing field.
A global network of central banks, each with its own laws and regulations but working in concert with CBDC platforms in all other nations that follow a typical process, is the result of the combination of tokenization and unified ledger.
The BIS was not the first organization to envision a CBDC program with global integration. China proposed a process for CBDCs in 2021 that outlines guidelines for their global application and information sharing.
A tokenized global financial system combines local bureaucracy with international autonomy. Internationally, there is no gatekeeper other than the widely accepted protocol; internally, the central government is in charge.
The idea of money would be transformed by a worldwide integrated CBDC platform. Real-time trading of various currencies and tangible asset tokens was seamless. Through difficulty, a unified ledger produces simplicity. There would only be two types of users: creditors and debtors.
The economic system’s automation opponents worry that CBDCs will bring about an Orwellian world. They point out that institutions may monitor people’s financial transactions. The hyper-transparency that is required to overcome fraud, corruption, and injustice, according to proponents of CBDCs, would be created.
On the plus side, each nation has the freedom to choose how to interact with international platforms and apply its own CBDC systems. The importance of autonomy and social governance. In nations with reduced levels of trust in the government, foe to CBDCs tends to be higher.