Notti Pet Food secures US$500K seed funding to elevate pet health & nutrition standards in Southeast Asia
- aspires to have 200 marketers both online and offline by the year 2024.
- Funding will help new product launches, rise into the Philippines &, Singapore

Notti Pet Food, the modern pioneer behind Southeast Asia’s first sluggish- baked super premium mealworms, has secured a seed funding of US$ 500, 000 ( RM2.4 million ) from 500 Global and First Move, marking a major step in the dataset company’s trip.
This innovative funding will help the business, which is focused on promoting South Asian animal health and nutrition standards, including launching new product lines and entering the Philippines and Singapore areas.
Over half of Malaysians ( 51.1 % ) currently own pets, according to Standard Insights ‘ most recent Consumer Report Malaysia 2023, which is expected to rise. As dog ownership grows, so does the need for animal food, with minimal higher- quality options available. Notti is a better option than traditional animal meals because of this trend. Their distinctive product line features 100 % individual- quality meat, enriched with fruit, vegetables, bacteria, and supplements.  ,
This distinguishes Notti from other corporate brands that rely on confusing labeling and meat meal. Notti preserves nutritional integrity by using genuine ingredients and a soft 90°C slow-baking technique, in contrast to the high-temperature extrusion techniques used by main brands.
Notti’s materials have received clinical testimonials, exceed global Association of American Feed Control Officials Nutrient Standards, and are suitable for all ages, species, and styles.
Keyee Yap, chairman of Notti Pet Food, emphasized,” Notti is more than just a product, it embodies our opinion that pets are cherished community members. My staff and I are dedicated to making sure your pets receive nutritious foods and an experience that recognizes the special relationship we share with them as a devoted animal lover, as well as myself.
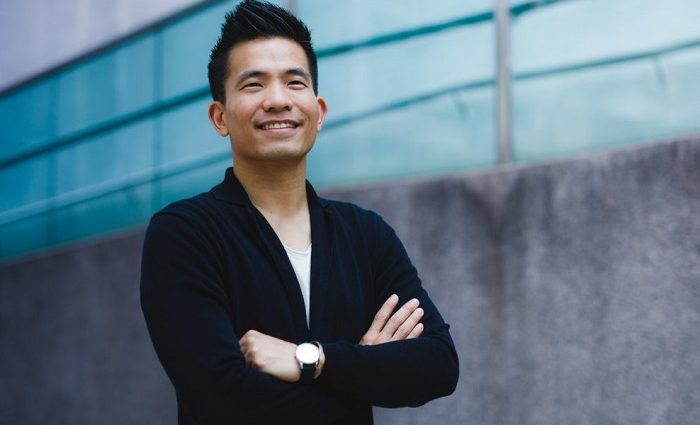
Khailee Ng ( pic ), managing partner at 500 Global, highlighted Notti’s team strengths:” Beyond being a pet food company, Notti is a pet- focused entity with a roadmap for multiple revenue streams and products. We’re eager to help their progress in the expanding pet industry because we’ve built related businesses for people.
Audra Pakalnyte, companion at First Move, noted Notti’s ability as she stated,” At First Move, we seek out founders with toughness, strong know- how, and enthusiasm, and Yap embodies all of these qualities. From our first meeting, it was clear that her commitment to solving real problems, innovating, and maintaining high standards in the pet industry was a driving force behind Notti. We’re excited to work with Notti as they continue to expand and have a significant impact.
Notti actively participates in Trap- Neuter- Return initiatives and charitable campaigns, including giving pet kibbles to animal shelters, in addition to advancing animal health and nutrition. Their focus on innovation, nutrition, and animal welfare reflects their mission to foster a healthier and more compassionate world.
Currently available in over 100 pet shops across Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, and the Philippines, Notti aims to expand to 200 online and offline distributors by the end of 2024, signaling confidence in driving substantial business growth and benefiting pets worldwide.





















.jpg)
 Cradle Fund Sdn Bhd, as the focal point company for Malaysia’s business habitat, lauded the efforts, noting that it is a testament to the work and strategic initiatives undertaken to develop a conducive atmosphere for startups. Companies are viewed by Malaysia as a crucial component of spurring local innovation and technological progress. Cradle aims to bring together all habitat partners ‘ resources and experience. With a consistent commitment to cultivating a high- performing, inclusive, globalised, and sustainable ecosystem, Cradle envisions propelling Malaysia to the forefront of the global startup ecosystem”, said Norman Matthieu Vanhaecke ( pic ), Group CEO of Cradle.
Cradle Fund Sdn Bhd, as the focal point company for Malaysia’s business habitat, lauded the efforts, noting that it is a testament to the work and strategic initiatives undertaken to develop a conducive atmosphere for startups. Companies are viewed by Malaysia as a crucial component of spurring local innovation and technological progress. Cradle aims to bring together all habitat partners ‘ resources and experience. With a consistent commitment to cultivating a high- performing, inclusive, globalised, and sustainable ecosystem, Cradle envisions propelling Malaysia to the forefront of the global startup ecosystem”, said Norman Matthieu Vanhaecke ( pic ), Group CEO of Cradle.


 The Practical Guide on VC and PE in Malaysia, according to Dr. Awang Adek Hussin, the president of the SC, is “our commitment to creating a conducive environment for funding and innovation. We want to create a more vibrant group of professional traders to assist entrepreneurs in Malaysia by providing quality on the business landscape for VC and PE firms.
The Practical Guide on VC and PE in Malaysia, according to Dr. Awang Adek Hussin, the president of the SC, is “our commitment to creating a conducive environment for funding and innovation. We want to create a more vibrant group of professional traders to assist entrepreneurs in Malaysia by providing quality on the business landscape for VC and PE firms.




.jpeg)