India and Pakistan: The first drone war between nuclear-armed neighbours
 NurPhoto via Getty Images
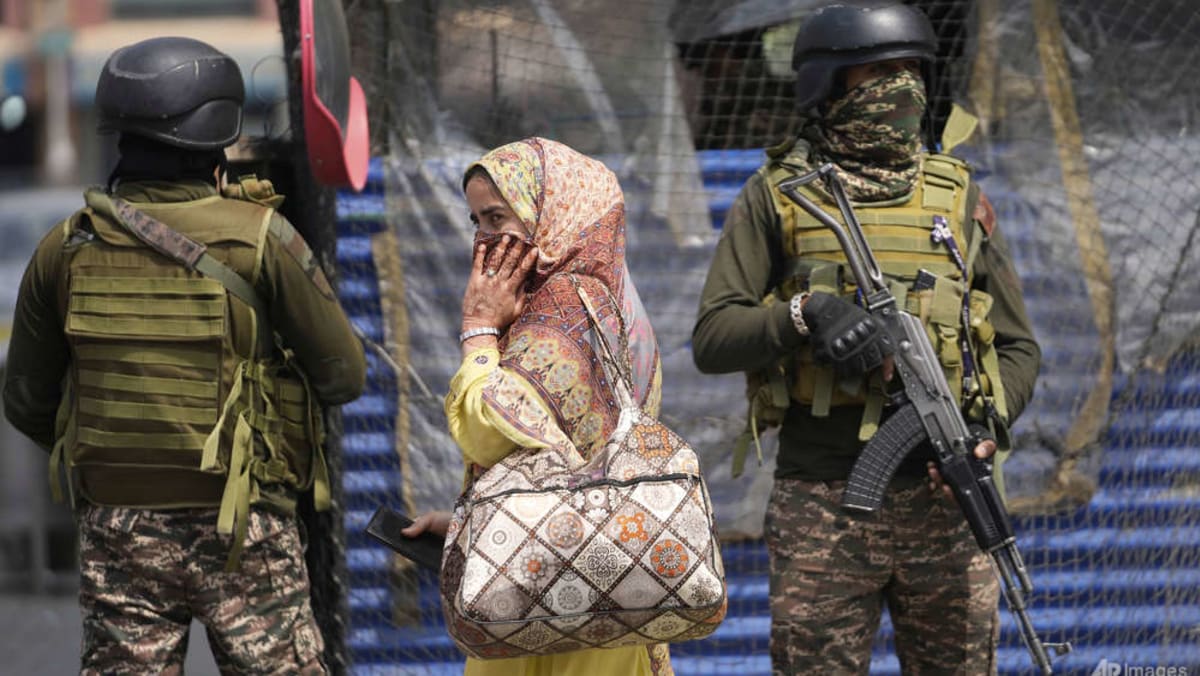
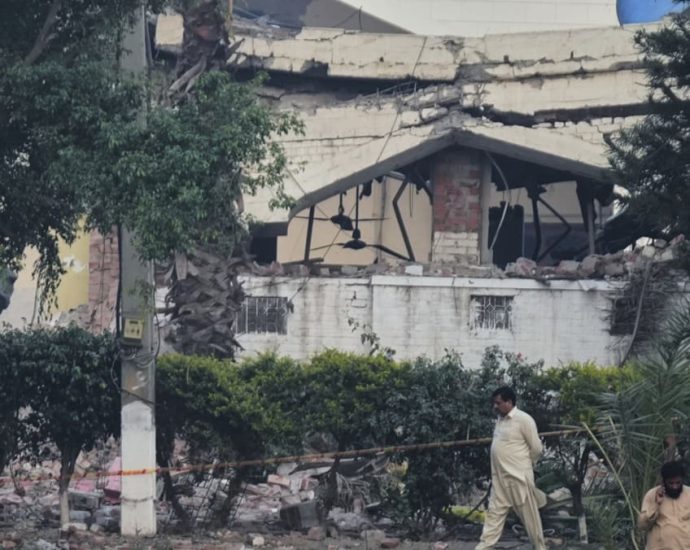
NurPhoto via Getty ImagesSouth Asia has seen the first aircraft war between neighbors with nuclear weapons ever.
India quickly refuted Islamabad’s claim that Pakistan had launched tides of drones and weapons at three military installations in Indian-administered Kashmir on Thursday.
Pakistan claimed to have shot over 25 Indian robots recently. Delhi kept a public oath. The tit-for-tat attacks, according to experts, indicate a risky new step in the decades-old conflict because both parties exchange unmanned weapons and not just artillery across a tense border.
The area is teetering on the verge of escalation, with drones- motionless, distant, and deniable- opening a new chapter in the India-Pakistan conflict as Washington and another world powers demand restraint.
The Indo-Pak discord is transitioning into a new helicopter era, one in which “invisible eyes” and autonomous precision does guide escalation or restraint. The part that masters drone war didn’t just see the field; they’ll design it, so says Jahara Matisek, a teacher at the US Naval War College, to the BBC.
Pakistan claims that 36 people have been killed and 57 others have been injured in Pakistan and Pakistan-administered Kashmir as a result of American air strikes and cross-border hearth since Wednesday day. On the other hand, the Indian troops reports at least 16 civilian casualties killed from Pakistani firing. India insists its missile storm was in response to a dangerous terrorist attack last month in Pahalgam, an incident that Islamabad denies any involvement in.
The Pakistani defense announced on Thursday that Karachi, Lahore, and Rawalpindi had been the sites of 25 American drone strikes. Using both professional and weapon-based measures, the apparently Israeli-made Harop uavs were presumably intercepted. India asserted that it had neutralized some Muslim air defense scanners and devices, including one in Lahore, which Islamabad denied.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesLaser-guided missiles and bombs, drones, and unmanned aerial vehicles ( UAVs ) have become crucial in contemporary warfare, significantly improving the precision and effectiveness of military operations. These can provide coordinates for airstrikes or, if equipped, immediately laser-designate targets, thereby facilitating quick wedding.
Robots can be used as decoys or as a means of disarming army air defenses by flying into disputed airspace to release enemy radar, which can then be intercepted by loitering drones or anti-radiation missiles. In their conflict, Ukraine and Russia both do it in this way. Drones are a force multiple in degrading enemy air defenses without risking guarded aircraft because of their double functions, targeting and triggering, says Prof. Matisek.
According to experts, India’s helicopter fleet is essentially composed of Israeli-made reconnaissance drones like the IAI Searcher and Heron, as well as Harpy and Harop loitering munitions, which double as missiles and can perform precision and autonomous reconnaissance. According to experts, The Harop, in particular, reflects a move toward high-value, precision-targeted war and highlights the growing significance of loitering munitions in contemporary issue.
According to researchers, the Heron serves as India’s “high-altitude eye in the sky” for both peacekeeping and combat operations. The IAI Searcher Mk II has a range of 300 kilometers ( 186 miles ), a service area of 7, 000 meters ( 23, 000 feet ), and is designed for front-line operations.
While many people think India’s combat aircraft numbers are still “moderate,” a recent$ 4 billion offer to buy 31 MQ-9B Predator drones from the US makes a significant increase in its reach potential. They can fly for 40 days and up to 40, 000 feet.
According to experts, India is also developing swarming aircraft techniques, which use large numbers of smaller UAVs to swarm air defenses and contaminate them, allowing more valuable resources to enter.
Ejaz Haider, a Lahore-based defense scientist, reported to the BBC that Pakistan’s aircraft fleet is “extensive and diverse” and includes both imported and indigenous systems.
He claimed that there are “over a thousand drones” in the inventory, which are produced by local manufacturers in China, Turkey, and other countries. The Taiwanese CH-4, the Turkish Bayraktar Akinci, and Pakistan’s personal Burraq and Shahpar robots are just a few examples of significant websites. Also, Pakistan has developed loitering weapons, which has increased its ability to strike.
 via Getty Images Anadolu
via Getty Images AnadoluAccording to Mr. Haider, the Pakistan Air Force ( PAF ) has been implementing unmanned systems successfully for nearly ten years. He added that a key area of focus is the creation of “loyal friend” robots, unmanned aerial vehicles that can communicate with manned aircraft.
According to Prof. Matisek,” India has relyed heavily on Pakistan’s professional assistance, which includes providing Harop and Heron drones, while an continuing arms race is highlighted by Pakistan’s rely on Turkey and Chinese platforms.”
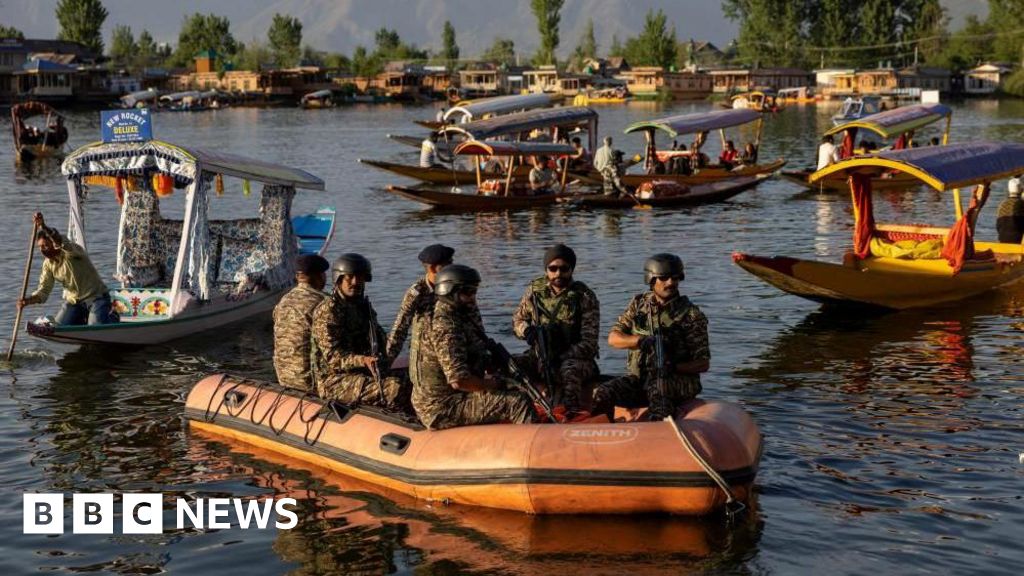
Experts claim that the current drone exchanges between India and Pakistan represent a significant intensification in their conflict. However, they are marked by significant differences from the drone-centric war that the Russia-Ukraine conflict witnessed. Both sides have deployed hundreds of UAVs for security, targeting, and immediate episodes that, making drones a key component of military operations.
A lower-level military option is to use drones [in the ongoing conflict ] rather than fighter planes or heavy weapons. Robots are less heavily armored than guarded aircraft, so in some ways this is a constrained move. The math completely changes, according to Manoj Joshi, an analyst for Indian defense, if this is just a precursor to a larger flying campaign.
Ejaz Haider says the recent aircraft action in Jammu “appears to be a military response to immediate actions, not a full-scale retaliation ] by Pakistan.”
” We may be shocked and awed in a real hostile strike against India.” It would probably be more extensive, involving a number of websites, both manned and unmanned, and aiming for a wider range of goals. According to Mr. Haider, a quite operation would aim to have a significant impact and send a signal of a major escalation beyond the present tit-for-tat exchanges.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesResearchers believe that robots ‘ impact on the Ukraine field has been more limited and symbolic than the one they have had. Both nations are using their guarded heat forces to launch missiles at one another as well.
According to Mr. Joshi,” the satellite war we’re witnessing may not last long; it could just be the start of a larger conflict.”
This could indicate either a de-escalation or an increase; both options are open to discussion. The course we should go in is questionable because we are at a turning point.
India’s drones are a clear fit for its precision-strike strategy, enabling stand-off targeting without the use of guarded aircraft across borders. Despite this progression, important questions still remain.
Drones reduce the social and operational bar for action, according to Prof. Matisek, by offering options to monitor and strike while attempting to lessen escalation risks.
” But they also introduce fresh increase dynamics: each helicopter that is shot down and whose detector is blind transforms into a potential battleground in this contentious environment between two nuclear powers.”