Huawei, a tech giant, is more ready than it was for Donald Trump’s subsequent assault on China.
More than punishment, the major risk to the bank’s sales and profits then appears to be the possibility of a tariff-induced crisis. Over 70 % of Huawei’s sales are currently made in China.
Huawei’s complete sales are almost at their pre-sanctions maximum, which is supported by a switch to local procurement. Its profits in the US are small, leaving virtually no immediate exposure to Trump’s taxes.
A sizable R&, D budget has allowed the business to stay at the top of the telecom equipment market while facilitating diversification into artificial intelligence ( AI), cloud computing, autonomous driving, and semiconductors. The balance sheet is noise.
Recall that, in May 2019, Trump banned US telecom carriers from using Huawei equipment and the Bureau of Industry and Security ( BIS ) of the US Department of Commerce put the company on its Entity List, preventing it from buying components and other products containing US technology without the department’s approval.
These regulations were put in place over the course of two years to prevent the company from receiving advanced semiconductors, especially those produced by Taiwan’s TSMC, the nation’s leading high-end device manufacturer.
Huawei even was unable to access Google’s Android programs, including Google and Google Maps, as well. This caused Huawei’s 5G mobile phone company to decline, resulting in a 29 % overall decline in sales in 2021 and sharp declines in its income before property sales.
After selling its Honor budget brand to protect it from US sanctions, Huawei’s share of the global cellphone market decreased from 18 % in 2019 to about 2 % in 2023.
But the base was that. Sales increased marginally in 2022, rose by nearly 10 % in 2023 and jumped 22 % in 2024, with sales of cellphones and other consumer products up 38 %. If non-core business profits are taken into account, gains also increased in 2023.

The geographical breakdown of Huawei’s revenue shows its rising dependency on the local Chinese market.
In 2019, the business was added to the Americas Entity List, and 59 % of its sales were made in China, 24 % in EMEA ( Europe, Middle East, and Africa ), 8.2 % in Asia-Pacific, 6.1 % in the Americas, and 2.7 % in other markets.
China had a breakdown of 71.4 %, followed by EMEA of 17.2 %, Asia-Pacific of 5 %, the Americas ( now primarily Latin America of 4.2 % ), and other regions of 2.2 % in 2024. Russia accounted for 15 %-20 % of EMEA sales.
Home sales increased by 30 % as a result of technological technology and the Chinese economy’s digitalization.
Progress across all of the company’s business segments was driven by strong demand for new design smartphones, telecoms network products, cloud computing, data storage, electric power, and related cars with self-driving functions.
Inside China, sales rise was highest in Russia, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, South Africa, Brazil and Indonesia.
Selling decreased in all of the nations where revenue of Huawei’s 5G telecoms equipment have been restricted or prohibited, including India, Germany, the UK, Canada, and Australia.

Restoring and diversifying
Huawei rebuilt its smartphone business by turning to Taiwanese semiconductor factory SMIC and developing its own Harmony running program.
HarmonyOS, which runs on a variety of devices, including smartphones, devices, tablet computers, TVs, electric cars, and IoT ( Internet of Things ) equipment, is currently second in China, trailing only Android and Apple’s iOS.
Huawei’s Mate 60 cellphone, which was released in August 2023, demonstrated that US sanctions are more of an opportunity for Chinese development than an unachievable barrier.
Based on a 7nm computer fabricated by SMIC without using ASML’s EUV printing, which cannot be sold in China, it was not supposed to be achievable. Gina Raimondo, a former secretary of commerce, described it as “incredibly disturbing.”
Huawei won the battle of the Chinese smartphone business in 2024, surpassing Apple’s iPhone and its local rivals, to regain control of the market, which saw its market share reach 18 % in the fourth quarter. But Huawei’s worldwide market share is still only about 6 %.
After the BIS ordered Oracle to stop providing Huawei with application updates and technical support, it was also forced to develop its own ERP ( Enterprise Resource Planning ) program.
It took more than three times before the enhanced edition without legacy issues that it now uses to support its own international businesses and also provides to Chinese state-owned companies like PetroChina and China Mobile as well as BYD, Xiaomi, and another privately held Chinese companies.
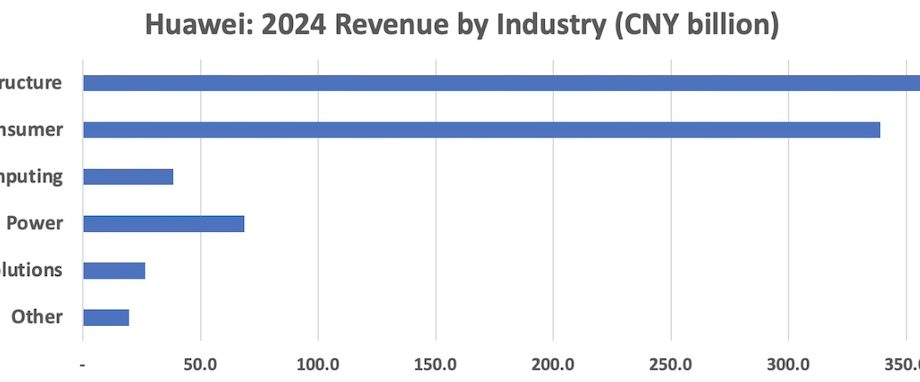
In 2024, Huawei’s efficiency by solution department was as follows:
Sales increased by 4.9 % to 42.9 % of the overall, mainly for ICT infrastructure. Basic stations, antennas, another mobile telecommunication system hardware and software, optical fiber and other fixed-line network equipment, enterprise switches and routers, 5G solutions for mining, seaports, and other particular industrial applications, as well as AI predicted maintenance.
Government spending and widespread use in industrial, logistics and social infrastructure applications support demand for 5G networking equipment in China. These factors, in addition to a comparatively uninteresting 5G consumer base in Europe and America, have increased Huawei’s share of the global market for radio access network products from 31 % in 2023 to an estimated 35 % in 2024.
China also has a strong investment in 6G, which should allow Huawei to continue receiving orders. It is also the world leader in the deployment of 5. 5G (5G-Advanced ) telecom services. South Korea, Japan, Finland, the EU and the US are also working on 6G, but China has the most supportive government and largest potential market.
China Mobile technology officer Liu Guangyi said in an interview with China Global Television Network ( CGTN) at the Global 6G Conference in Nanjing on April 10 that:”…
” When we first created 5G about a decade ago, we didn’t anticipate the rapid expansion of artificial intelligence. The focus then was mainly on improving communication speed and efficiency. However, by doing so, we ignored the potential for incorporating additional capabilities.
Think about intelligent hardware, connected vehicles, and robotics. 6G networks can help make these technologies more lightweight, compact, and low-cost, making mass adoption more feasible and accelerating the intelligent transformation of society.”
Consumer goods: Sales increased by 38.3 %, making up 39.3 % of the total. Smartphones and HarmonyOS, laptop and tablet computers, smartwatches and fitness trackers, and smart home appliances are some of the products offered.
Market research organization Counterpoint reports 36 % growth in Huawei’s smartphone shipments in 2024, with a higher average selling price boosting the value of sales.
Sales of cloud computing increased by 8.5 %, or 4.5 % of the total in 2024. Large language models for manufacturing, logistics, and finance, AI model training and security, database services, and software-as-a-service, including video conferencing in competition with Zoom and Microsoft Teams, are among the products offered.
Huawei was the second largest provider of cloud services in China last year, with a market share estimated at 22 % versus 34 % for Alibaba and 18 % for Tencent, according the market research organizations and industry sources. With a market share of about 5 %, Huawei came in fifth overall.
Digital power: Sales were up 24.4 % to account for 8 % of the total in 2024. Inverters, battery storage, AI efficiency optimization, and power grid integration for solar energy, data center power supplies and cooling systems, motor/powertrain design for electric vehicles, mobile telecom base station power supplies, lithium-ion batteries for telecom, renewable energy and microgrids, and cloud-computing energy management systems are some of the products.
Huawei creates prefabricated modular data centers that are housed in dust, water, extreme temperatures, and shock-proof metal containers the size of shipping containers for remote and harsh environments. Dozens of these modular data centers have been deployed in Saudi Arabia.
Automotive products: Sales increased by 5.7 times to account for 7.1 % of the total in 2024. Products include integrated motor/inverter systems and HarmonyOS for vehicles, as well as the Pangu AI model for urban and highway driving.
These are provided to several Chinese automakers. According to market research firms and industry sources, Huawei’s share of China’s market for autonomous vehicle technology is between 25 % and 30 %.
Other goods: In 2024, sales increased by 70.0 % to 5.8 % total. Medical devices, industrial sensors, 5G modems for use with robots and drones, augmented reality glasses and displays, and other products that do not fit conveniently into other segments.

Huawei’s R&, D budget has increased from 15 % to 20 % of its sales since 2021, up from 15 % to 15 % in the prior two years.
The company spent a lot of money on advanced semiconductor technology, the HarmonyOS NEXT mobile operating system, 6G, and quantum computing, but the figure for 2024 as a whole increased to 20.8 %, but in Q4 it increased to 25 %.
In addition, it recorded expenses related to the replacement of imported components with Chinese alternatives and the cancellation of contracts in Europe due to sanctions, wrote down 4G inventory, and cut prices to compete with Apple, Alibaba and Tencent.
In the end, net profit fell to zero in the fourth quarter of the year as a result. However, the financial decks were cleared for what appears to be a challenging 2025 and the full-year results were in line with management’s expectations.
Follow this writer on , X: @ScottFo83517667