Thailand, Australia target global crime

Thai and Asian authorities have launched a joint operation to demolish transnational criminal systems in a significant step toward preventing international murder. The collaboration aims to address complex crimes that transcend borders, from cocaine to child abuse and cryptocurrency-based money fraud.
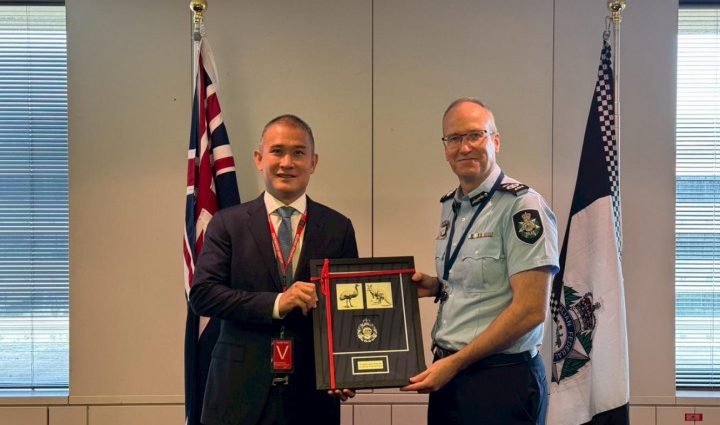
Pol Lt Gen Jirabhop Bhuridej, Commissioner of the Royal Thai Police’s Central Investigation Bureau ( CIB ), led a delegation to Australia earlier this month for discussions with its law enforcement counterpart, the Australian Federal Police ( AFP).
According to Pol Lt Gen Jirabhop,” the nature of international crime nowadays demands real-time cleverness, cross-border cooperation, and scientific integration.” ” We are no longer focusing on isolated businesses. Our goal is to create a co-operative system that is flawless.
Both sides came to terms with the necessity of creating shared task forces and information-sharing procedures during the visit. Thailand’s officers displayed their skills in industry operations and local knowledge, especially in the Greater Mekong Subregion, while the AFP introduced tools and systems developed for international crime surveillance.
He claimed that the Australians liked how quickly we operated. Our officers are trained to manage challenging terrain and access challenging locations, which are frequently the hub of these legal networks.
Digital Trails, Drug Routes
One of the main points of discussion was drug smuggling. Thailand, a long-standing transport nation, is a key player in the transition from Myanmar’s Shan State’s manufacturing hubs to Australia’s high-value markets.
” Crystal meth, or “ya glacier,” continues to be the main drug coming into Australia from Southeast Asia,” remarked Pol Lt. Gen. Jirabhop. It’s inexpensive to produce, high-quality, and low, which makes it very beneficial for organized crime organizations.
Another medications, such as cocaine and MDMA, are still popular among those who are younger and in the heart of entertainment. Despite the knowledge shared by the AFP, medications are frequently kept hidden inside reasonable shipping pots filled with gadgets, household items, or car parts, a tactic used to obstruct border inspections.
Thailand and Australia are looking into preventing actions in response, including sharing information on known traffickers and trafficking routes and improved goods screening. The possible development of a joint databases that both countries can use to track supplies and suspects in real-time is a key growth.
The conflict goes way beyond traditional contraband, though. Today’s criminal organizations are becoming more tech-savvy, frequently laundering profits using electronic money and online wallets. He claimed that” criptocurrency is the new frontier for criminals.” They” industry anonymously, move money immediately, and escape conventional financial oversight,” they claim.
Thailand also faces legitimate and structural restrictions, despite the AFP’s advanced crypto-tracking technology. Digital property lack a clear position as admissible evidence in Thai law, putting a strain on efforts to freeze or acquire funds.
” Despite the difficulties, we are moving forward,” he said. To tighten controls on illicit money flows, we are working with partners like Interpol ( International Criminal Police Organization ), Aseanapol ( Association of Southeast Asian Nations Chiefs of Police ), and financial intelligence organizations like Amlo ( Anti-Money Laundering Office ) and Austrac ( Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre ).
Both nations are investing in the future of law enforcement through engineering, management training, and inter-agency cooperation, in addition to their functional work. Data management is a promising area of cooperation. The AFP, which has developed related methods for predicted surveillance and case integration, is of particular attention to the CIB’s Big Data Centre.
We had in-depth debate about Thailand’s Big Data Center and how it could work with the AFP’s Investigation Management System, according to Pol Lt Gen Jirabhop. There are many things that we can understand from one another, particularly in terms of system infrastructure and software in real-world situations.
The American Criminal Intelligence Commission, which manages the nation’s potent database that connects crime data from across Australia, received similar industrial synergies during discussions with them.
” We think this is a concept that is for replicating,” said Pol Lt. Gen. Jirabhop. ” Centralizing crime data prevents effort duplication because it allows companies to answer more quickly, identify patterns sooner, and prevent duplication.”
Leadership growth was also high on the plan. To discuss leadership training programs, Thai officials met with the Australian Institute of Police Management ( AIPM). Programs are being made to take Thai officers to AIPM for superior training, and to invite American trainers to Thailand to share their experience. He claimed that “effective policing depends on good leadership.” It’s about creating institutions that can adapt, innovate, and lead in a fast-changing world, not just about catching criminals.
The Joint Policing Cybercrime Coordination Centre ( JPC3 ), an Australian multi-agency hub that brings together police, cybercrime experts, banks, and tech companies in one location with shared databases and real-time coordination, is a standout example of innovation.
He claimed that it provides the kind of integrated approach we require. We want to use this model in Thailand to combat cybercrime and financial crime more effectively.
Security Partnership
Thailand and Australia’s shared commitment to public safety is emerging as a cornerstone of regional stability as transnational criminal threats become more sophisticated.
Both of our countries are clearly facing common threats, according to Pol Lt. Gen. Jirabhop. By uniting through joint operations, intelligence sharing, and institutional development, we convey to criminal networks that we are prepared, connected, and resolute.
Both parties are optimistic about the plans to formalize this cooperation through more structured frameworks and regular exchanges. As crime continues to become more global, so must the response. ” This is only the beginning,” Pol Lt. Gen. Jirabhop declared. A partnership for peace, safety, and justice across our nations is something we’re building that will endure.