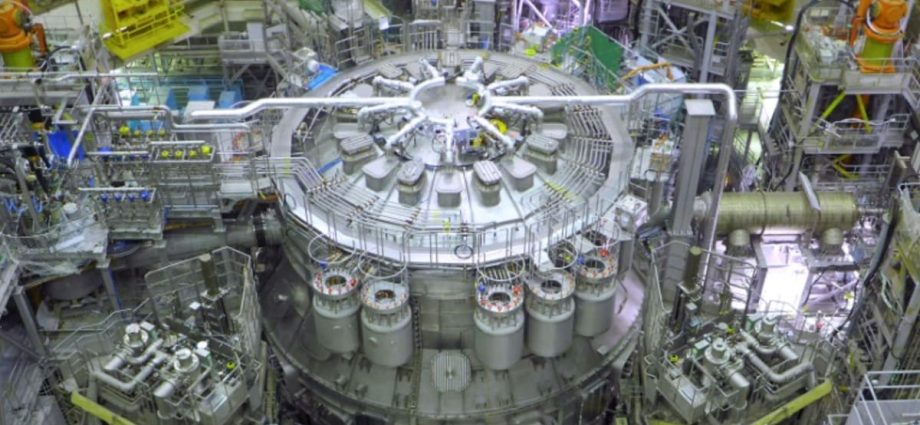
Researchers at ITER, which is over budget, behind schedule and facing major technical problems, hope to achieve nuclear fusion technology’s holy grail, net energy.
Sam Davis, deputy project leader for the JT-60SA, said the device will “bring us closer to fusion energy”.
“It’s the result of a collaboration between more than 500 scientists and engineers and more than 70 companies throughout Europe and Japan,” Davis said at Friday’s inauguration.
EU energy commissioner Kadri Simson said the JT-60SA was “the most advanced tokamak in the world”, calling the start of operations “a milestone for fusion history”.
“Fusion has the potential to become a key component for energy mix in the second half of this century,” Simson added.
The feat of “net energy gain” was managed last December at the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the United States, home to the world’s largest laser.
The US facility uses a different method to ITER and the JT-60SA known as inertial confinement fusion, in which high-energy lasers are directed simultaneously into a thimble-sized cylinder containing hydrogen.
The US government called the result a “landmark achievement” in the quest for a source of unlimited, clean power and an end to reliance on carbon-emitting fossil fuels that cause climate change as well as geopolitical upheaval.
Unlike fission, fusion carries no risk of catastrophic nuclear accidents – like that seen in Fukushima in Japan in 2011 – and produces far less radioactive waste than current power plants, its exponents say.