‘This is what I want to do, mum’ – New Zealand’s World Cup legacy
“I’m really filled with hope,” says New Zealand women’s football fan Annie Kennedy. “There is belief that wasn’t there before. I see it as a huge success.”
New Zealand’s biggest sporting global party has finished.
With co-hosts Australia staging the second semi-final, third place play-off and final, the 29th and final Fifa Women’s World Cup match to be staged in New Zealand saw Spain defeat Sweden 2-1 in Tuesday’s semi-final at Eden Park.
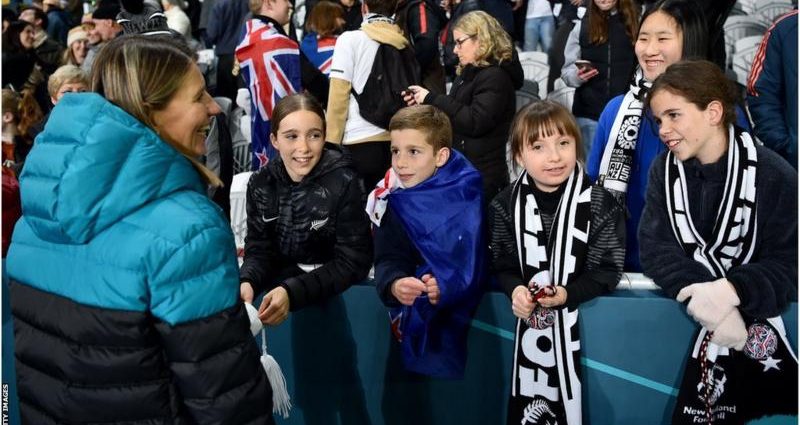
Another 43,217 sell-out crowd watched as all three goals came in a dramatic final nine minutes before La Roja’s celebrations began after reaching the final for the first time.
A pulsating end to a five week festival of women’s football in New Zealand.
From Auckland to Wellington and Hamilton to Dunedin, crowds have clapped, cheered and marvelled at the skills of global stars like Alexia Putellas, Alex Morgan, Ada Hegerberg and Fridolina Rolfo.
Eden Park witnessed the first of many shocks at this unpredictable tournament when New Zealand’s Football Ferns defeated former world champions Norway on an unforgettable opening night on 20 July.
South Africa’s players sang and danced as they stepped off the team coach in Dunedin, while Japan’s left a ‘thank you’ message on a white board after cleaning their dressing room in Wellington.
But what impact has the Women’s World Cup had in New Zealand? And what does the future of women’s football in the country look like now teams have packed up and camera lights been dimmed?

‘Never seen anything like it’
Michael Burgess is an experienced sports writer for the New Zealand Herald newspaper.
“We have never seen anything like this before and all of us realise we probably won’t see anything like it again,” he told the BBC World Football at the Women’s World Cup podcast.
“Football has taken over the country in an unprecedented way. We felt so lucky to get this tournament in the first place and, with the way women’s football is growing around the world, it probably won’t come back to Australasia.”
In a country with a population of just five million people, rugby and cricket dominates the sporting landscape in New Zealand.
Is football catching up?
“The Football Ferns took rugby off the back pages,” added Burgess. “Even after they were knocked out it just continued and it was something none of us really expected.
“It been an awakening for the sport – especially for the women’s side of the game.”
There are challenges ahead for New Zealand Football, the country’s governing body, as it looks to build on the success of the Women’s World Cup.
“There will be a lot of kids who have seen the Women’s World Cup who will say ‘this is what I want to do, mum’,” said Burgess.
“Are the clubs available? Are pitches available? Are coaches available? Another challenge is that we don’t have a women’s professional league in New Zealand.
“Netball is the massive female sport in this country. I can certainly see a migration from sports like netball and hockey and other traditional female sports into football. If you get the numbers, that starts to pay off in so many ways.”
‘Starved of football’
Before the World Cup, the record crowd for football match in New Zealand was 37,034 for a men’s World Cup play-off against Peru in Wellington in 2017.
Despite early concerns about ticket sales, that record has been shattered three times at Eden Park, New Zealand’s national stadium, during this tournament.
After 42,137 witnessed Hannah Wilkinson’s winner for the Football Ferns against Norway in Auckland, 42,958 turned up to see the USA held 0-0 by Portugal on 1 August. Four days later that sell-out crow of 43,217 witnessed Spain thrash Switzerland 5-1 in the last 16 – the biggest stadium crowd for a sporting event in New Zealand this year.
Eden Park was also sold-out for the quarter-final between Japan and Sweden on 11 August and Tuesday’s semi-final.
Around 80% of the ticket sales for Eden Park have been to people living in New Zealand.
“This tournament has seen a colossal change in the way football and particularly women’s football is seen in New Zealand,” Andrew Pragnell, CEO of New Zealand Football, said.
“Football is already the biggest and the fastest growing organised team sport in the country and this tournament, as well as the numerous legacy programmes we have established, will supercharge it.”
More than 700,000 fans watched the 29 World Cup games in New Zealand, with Wellington Regional Stadium hosting nine matches.
“It seemed like a distant dream in the dark days of Covid,” Shane Harmon, CEO of Wellington Regional Stadium, said.
“Any concerns prior to the tournament about whether Kiwis would get behind this event in sufficient numbers have been firmly put to rest.”
Nick Sautner, CEO of Eden Park, which also hosted nine matches, said Kiwis had been “starved of football content” before the World Cup.
“The atmosphere at Eden Park has been electric, with colour and culture celebrated through the beautiful game,” he added.

‘Massive jump in numbers’
When New Zealand was named co-hosts for the Women’s World Cup in June 2020, there were no professional women’s football teams in the country.
Since the announcement, Wellington Phoenix have joined Australia’s A-League Women.
They play their home games at Wellington Regional Stadium, one of 10 venues used at the World Cup.
“Not long ago we had about 11 girls at the academy. Now we’re getting emails every day from girls who dream of becoming professional players,” Katie Barrott, female development lead at Wellington Phoenix academy, told the BBC World Football podcast.
While there is disappointment here that New Zealand failed to advance from their World Cup group, the Football Ferns managed four points from three games – more than in their previous five World Cup campaigns combined (3).
“Everybody is talking about the Football Ferns,” said Paul Temple, Wellington Phoenix women’s head coach.
“Everyone knows who they are and we’ve now got domestic role models for our young girls to look up to.
“I heard [England’s] Leah Williamson talk about when she was growing up and not having those female players to see every week on television. It was the male players who were the heroes.
“I’m sure we’re going to see a massive jump in numbers of young girls wanting to play after this World Cup.
“We’ll hopefully see the effects of that swell in three of four years time. That legacy is so important.”

Will World Cup leave lasting legacy?
Charli Dunn is a 16-year-old centre-back for Auckland-based club Western Springs, whose facilities were used by Norway.
She has to actively promote football to her friends.
“Especially girls’ football, you have to promote that a lot over boys football, rugby or something,” she said.
“But I think most people are kind of getting more into the football because the World Cup’s been here.”
Caleb Ward, interim women’s coach at Western Springs, added: “I think women’s soccer has a really bright future.
“To see New Zealanders start to embrace it is really cool, and hopefully we get the knock-on effect of more people participating.”





















